Data Annotations - MaxLength Attribute in EF 6 & EF Core
The MaxLength attribute specifies the maximum length of data value allowed for a property which in turn sets the size of a corresponding column in the database. It can be applied to the string or byte[] properties of an entity.
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations; public class Student { public int StudentID { get; set; } [MaxLength(50)] public string StudentName { get; set; } }
In the above example, the MaxLength(50) attribute is applied on the StudentName property which specifies that the value of StudentName property cannot be more than 50 characters long.
This will create a StudentName column with nvarchar(50) size in the SQL Server database, as shown below.
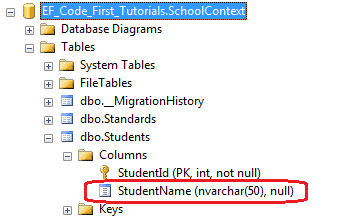
Entity Framework also validates the value of a property for the MaxLength attribute if you set a value higher than the specified size.
For example, if you set more than 50 characters long string value, then EF 6 will throw System.Data.Entity.Validation.DbEntityValidationException and EF Core will throw Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.DbUpdateException.
Note: The MaxLength attribute can also be used in ASP.NET MVC to validate the value of a property. Visit Implement Validations in ASP.NET MVC for more information.